Breastbone (Sternum): Anatomy, Fracture and Important Clinical Conditions
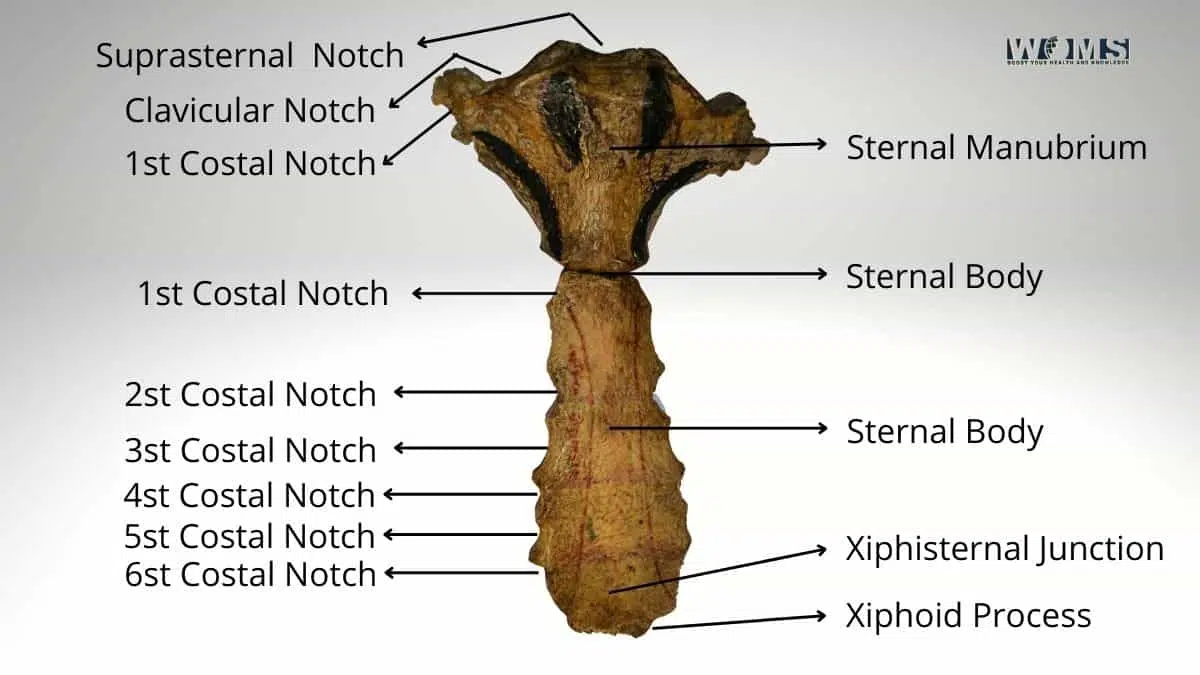
The breastbone is the most important structure of the human body, as it protects and supports all other structures in the chest cavity. It is also called the sternum or manubrium. It has a long narrow shape with two ends curved inward toward each other. It comprises three parts: the xiphoid process, the costal cartilages (ribs), and the sternum proper.
The xiphoid process is attached to the sternum at the Centre of its length. It is shaped like a small wedge-shaped piece of bone. The ribs attach to it on either side of the xiphoid process. The sternum is connected to the by ligaments. This allows for movement between the two bones. The sternum is divided into four sections:
- The upper portion contains the manubrium.
- The middle section contains the xiphoid process.
- The lower portion contains the body of the sternum.
- The xiphoid process connects the body of the sterna to the manubrium.
Anatomy of the breastbone
The breastbone consists of three main components: the xiphoid, the rib cage, and the sternum. The xiphoid is located near the Centre. It is a small triangular projection from the sternum. It serves as an attachment point for several muscles.
The xiphoid processes are usually covered by skin, but they can be seen through the skin when the person is lying down. The xiphoid may be broken during certain types of injuries. The xiphoid bone is often fractured along with the clavicle, another part of the collarbone. The xiphoid pressure is a small triangular projection between the second and third ribs. It helps support the heart and lungs.
Structure
The xiphoid process is a triangular bony projection located just below the sternoclavicular joint. The xiphoid forms part of the sternum. The sternal end of the xiphoid attaches to the manubrium of the sternum. There are five pairs of ribs, one pair on each side of the thorax. These ribs are joined together by cartilage and connect to the sternum.
The first rib is the longest and runs parallel to the spine. The second and third ribs are shorter and run perpendicular to the spine. The fourth and fifth ribs are smaller than the others and run obliquely across the back. The xiphoid lies between the second and third rib. The xiphoid provides stability to the sternum.
Costal Cartilages
The costal cartilages form the walls of the chest cavity. They provide structural strength to the ribcage. The ribs attach to the costal cartilages. The costal cartilaginous ends of the ribs are called the costochondral junctions. Costal cartilages are thin plates of the cartilage covering the ribs’ inner surface. Each rib has two parts: the upper portion (the body) and the lower portion (the arch). The costal cartilages are attached at their outer edges to the sternum. Their inner edge connects to the vertebrae.
The costal cartilage is made up of fibrocartilage. Fibrocartilage is a type of tissue that contains collagen fibres and elastic fibres. Collagen is a protein that gives structure to tissues. Elastic fibres are found in tendons and ligaments. The costal cartilages are also known as the costal arches. The costal arches are located between the ribs. The arches are connected to the sternum. There is a space between the arches called the intercostal space. This space allows the lungs to expand. The intercostal spaces are filled with fat.
Structure Of The Ribs
Ribs are curved bones that protect the organs inside the chest. The ribs are divided into three sections: the cervical, dorsal, and lumbar regions. The cervical region is located above the collar bone. It consists of seven bones. The dorsal region is located directly beneath the shoulder blade. It consists of 12 bones.
The lumbar region is located below the bottom of the spine. It consists of five bones. The ribs are covered by skin and muscle. The muscles are attached to the ribs on the outside. The ribs are held together by connective tissue. Connective tissue is a mesh-like material that holds structures together. The ribs contain many holes called foramina. These foramina allow nerves to pass through the ribs.
Ribs And Lungs
The ribs are connected to the lung sacs. The lung sacs are large bags that hold air. Air enters the lungs through the trachea. The lungs are located behind the heart. They consist of several lobes. The main lobe of each lung is called the left or right lung. The lobes of the lungs are separated by pleura. Pleura is a layer of connective tissue that covers the lungs.
The pleural membrane is a double layer of dense connective tissue. The pleura separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. The pleura lines the entire length of the lungs. The pleura surrounds the lungs like an envelope. The pleura is continuous with the peritoneum. The peritoneum is a membrane that lines the abdomen. When the lungs inflate, they push against the pleura. The diaphragm moves down when the lungs inflate. This movement pushes the stomach outwards.
Causes of breastbone fracture
A breastbone fracture can occur during childbirth. A fall on it can cause it’s fracture. Other causes include car accidents, sports injuries, and work-related injuries. People who have had surgery on this bone may be more likely to suffer a fracture. Fractures of this bone are usually treated surgically. Surgery is necessary if it is broken in multiple places. If the bone is broken only once, it can heal itself. In some cases, however, the injury requires surgical repair.
Symptoms
Pain occurs when a person suffers a breastbone fracture. Pain often starts after a fall. Sometimes pain begins before a fall. Pain may radiate from the area around the bone. Symptoms may last for weeks or months. Some people feel no pain. Others experience sharp stabbing pains.
Treatment
Treatment options for breastbone fractures depend on how much damage was done to the bone. Smaller breaks can be repaired without surgery. Larger breaks require surgery. Surgical treatment includes removing damaged pieces of the breastbone. Surgeons use screws, wires, or plates to hold the pieces together. After surgery, patients wear a cast for six to eight weeks. Patients must avoid strenuous activity for at least four weeks.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing breastbone fractures involves taking medical history information and performing physical examinations. X-rays determine whether there has been any damage to other body parts. Doctors also take x-ray pictures of the skull.
Prevention
To prevent breastbone fractures, people should not engage in fall activities. Children should always wear safety belts while riding in cars. Adults should never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Drivers should slow down and pay attention when driving. Wearing seatbelts reduces the risk of serious injury in automobile crashes.
Conclusion
The breastbone is one of the important parts of our body. It can lead to death if they aren’t treated properly. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help immediately if you experience chest pain. We need to keep this bone-healthy, so we don’t face any complications.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
How does a breastbone fracture happen?
A breastbone fracture happens when a person falls on their chest. A breastbone fracture can be caused by a fall from a standing height. It can also result from being hit in the chest. The force of the blow can break bones. A breastbone fracture is most common among children.
Is a breastbone fractured painful?
Yes, a breastbone fracture is painful. When someone falls on their breastbone, they will probably feel intense pain. The pain can start immediately after the fall. It may get worse as time passes.
What causes chest pain on the left side above the breast?
Chest pain on the left side above the breast can be caused by many things, including lung problems such as pneumonia. However, it can also be caused by heart problems.
How do you know if chest pain is muscle or lung?
If your chest pain comes and goes with breathing, it could be due to a lung problem. But if your chest pain doesn’t go away even after you breathe deeply, it’s more likely due to a muscle problem.
Can a broken breastbone be fatal?
No, a broken breastbone cannot be fatal. However, it can cause severe injuries to internal organs like the lungs, stomach, liver, spleen, intestines, kidneys, and bladder.
What are the symptoms of a breastbone fracture?
Symptoms of a breastbone include chest pain on the left side over the breastbone area. This pain usually starts suddenly and gets worse within minutes. Other symptoms include:
• Difficulty breathing.
• Coughing up blood, dizziness, fainting, nausea, vomiting.
• Shortness of breath.
• Swelling around the eyes.
• Weakness.
Can a breastbone fracture be treated at home?
Home remedies for it’s fracture include using ice packs, applying heat packs, and elevating the injured part of the body. You can also use cold compresses to reduce swelling and relieve pain. Sometimes, an ambulance may be called to take the patient to a hospital emergency room.