Big and Small Penis image: Anatomy and medical conditions
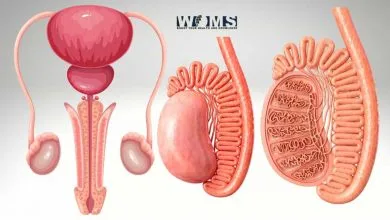
This article explains the anatomical details to describe all the associated features related to the penis using penis image. The penis is the copulatory or reproductive organ in the male members of higher vertebrates. In mammals, it also provides a tract for the passage of urine outside the body. It reaches its maximum size during the peak pubertal phase. The human anatomy of the penis image includes all the micro and macro information with some associated medical conditions.
Gross Anatomy of the penis
The penis consists of three main structural units. These are as follows:
- Radix – root
- Shaft – body
- Glans
Besides these three structures, the penis also contains three main tissues that are helpful in the erection. These erectile tissues include the corpus spongiosum and two corpora cavernosa. In addition, the penis is a common junction between the urinary and reproductive systems because of the presence of the urethra. Let us have a detailed look at the anatomical details of the penis image.
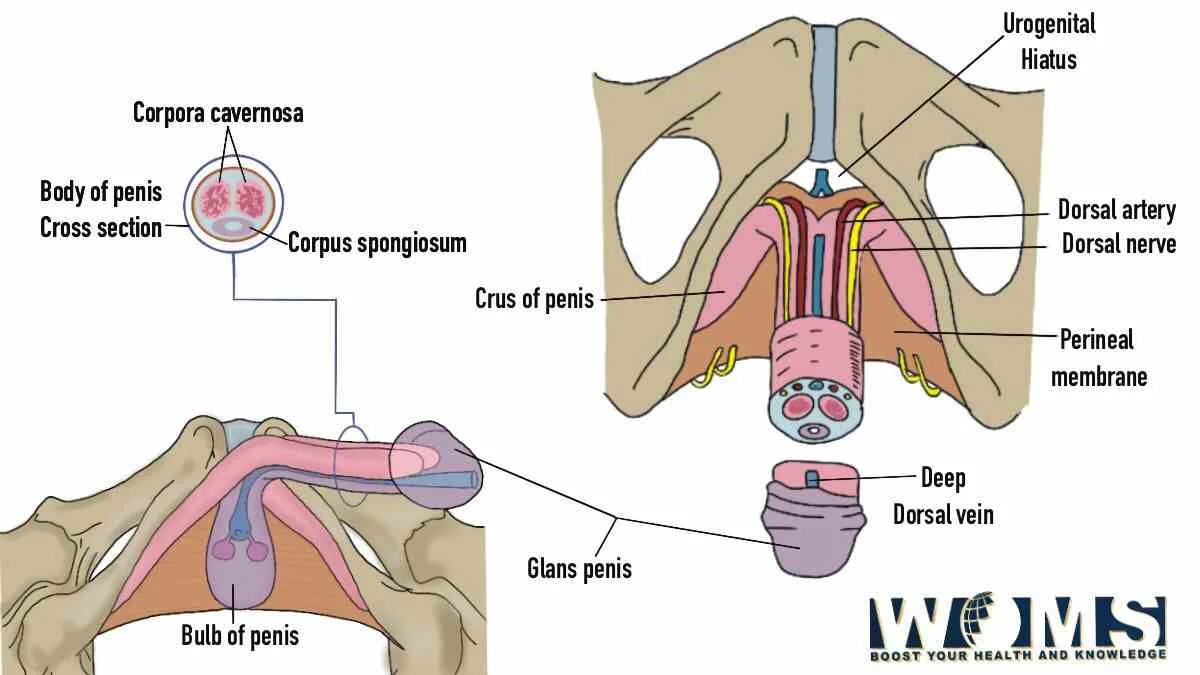
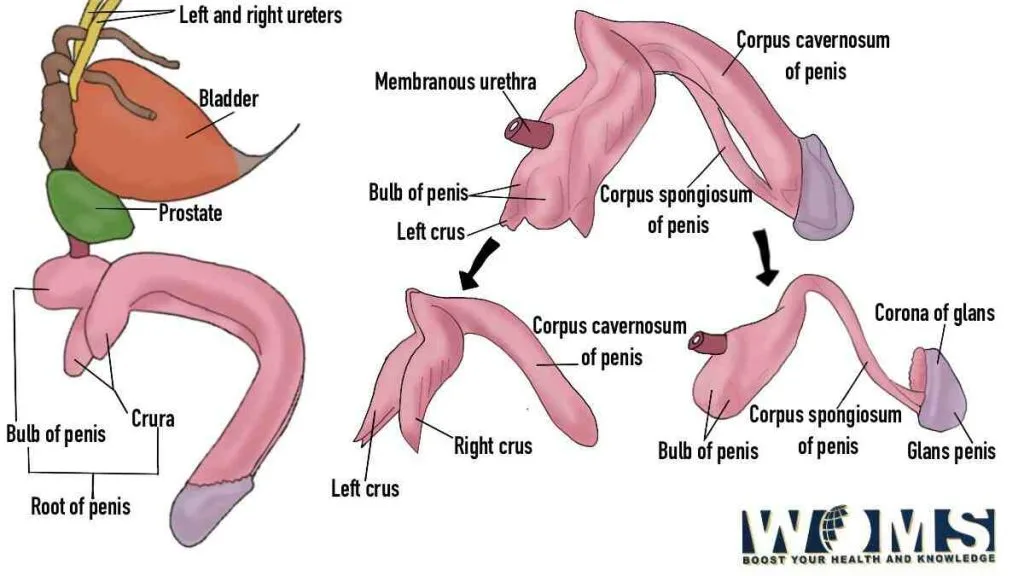
Root of the penis
It is the most proximal part of the penis present in the urogenital triangle of the perineum. It is attached to the public symphysis through the two suspensory ligaments. There are two muscles associated with the root of the penis. In addition, there are two erectile tissues including two crura of the penis and a bulb of the penis.
The crura of the penis are the extension of the corpora cavernosa proximally. Whereas, the bulb of the penis is an expansion of the corpus spongiosum proximally. It is present between the two crura of the penis. The bulb of the penis extends proximally as bulbospongiosus muscle as seen in the penis image.
Shaft of the penis:
The body or shaft of the penis is a freely moveable part just like a pendulum. This structure is entirely made of the skin layer. Under the skin layers, this structure contains three fasciae that surround the penis contents. Moving from deep to superficial, these fasciae are tunica albuginea, the deep fascia of the penis, and the superficial fascia of the penis. In addition, it also includes three Erectile tissues that are two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum.
Glans
It is the endpoint of the penis in the distal direction as seen in the penis image. It achieves its original shape due to the bulbous expansion of the corpus spongiosum. It also contains a urethral opening to pass out urine and semen outside the body.
What are erectile tissues?
Erectile tissues are those that help to till the penis with blood during the erection or stimulation phase. In the root, the erectile tissues are in the form of the right and left crura and the bulb of the penis. The right and left crura extend towards the body of the penis and continue as two corpora cavernosa. In contrast, the bulb of the penis extends to form the corpus spongiosum. Moreover, the urethra also runs along the corpus spongiosum. The corpus spongiosum expands in a bulbous manner to provide a proper shape to the glans of the penis. In the below given penis image, the erectile tissue of penis is demonstrated.
What are the muscles associated with the penis image?
There are two main muscles associated with the penis image. These are as follows:
- Ischiocavernosus – This muscle surrounds the right and left crura which are the erectile tissues. It helps in the erection of the penis by providing a contraction force in the crura to pass blood into the corpora cavernosa.
- Bulbospongiosus – As the name indicates, this muscle surrounds the bulb of the penis. It provides a contractile force to the urethra to pass out any residual urine and semen. You can use the penis image to check this muscle.
Ligaments associated with the penis image
There are two main ligaments associated with the penis image. These are as follows:
- Fundiform ligament – This ligament offers a supporting force to the penis and covers it like a sling. It is a condensation of the deep fascia.
- Suspensory ligament – This ligament supports the penis and makes it closer to the pubic bone. Moreover, it also provides support to the penis during erection.
Functions of the penis
The penis, being an external reproductive organ in the male, performs different functions. It has an important reproductive function along with the testicles. There are two main functions associated with the penis. These are as follows:
- Being a reproductive organ, it is one of the main structures during sexual intercourse. After erotic stimulation, the penis becomes erect. It becomes engorged with sufficient blood supply. The emission process, which is the mixing of the semen in the prostatic urethra, occurs before ejaculation. The semen expels out of the urethra from the external urethral orifice as seen in penis image. After remission, the penis comes back to its normal, relaxed position. In this way, the penis performs a primary function during sexual activity.
- The penis also plays a prime role in the urinary system. Men share the common passage for urine and semen. The penis also contains the urethra. The urethra is the main part to excrete urine out of the body. It carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice as seen in penis image. From this point, the urine passes out from the body. These facts can be demonstrated using the penis image.
Blood supply of the penis
The penis receives its arterial blood supply through the internal pudendal artery. It is one of the branches of the internal iliac artery. This artery encroaches the penis through Alcock’s canal. After entering, it divides into the common penile and perineal arteries. The common penile artery gives three branches that supply the deeper structures of the penis. The blood supply can also be related to the dry skin on penis. You can use the penis image to demonstrate the deeper structure of the penis. These branches are as follows:
- Artery of bulb of the penis – As the name indicates, it supplies the whole bulb of the penis and extends up to the glans. It also supplies blood to the penile urethra.
- Cavernous or deep artery of the penis – It is a paired artery that passes through the corpus cavernosum. Along its course, it also gives branches like straight and helicine arteries. These arteries directly reach into the sinusoids of the corpora cavernosa.
- Dorsal artery of the penis – This artery passes from the dorsal groove present between the corpora cavernosa. In addition, this artery extends into depth up to the deep penile fascia. In its way, it divides into several circumferential branches. Through these branches, this artery supplies to the corpora cavernosa.
Moreover, the perineal artery supplies blood to the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles.
Venous drainage:
The penis empties deoxygenated blood in three different ways. These are as follows:
- Superficial Venous system – This system contains the superficial veins of the penis that encroaches the dartos fascia of the penis. The skin of the penile shaft and prepuce drains its blood into this Venous system. This system, at the level of the penile shaft, combines with the single superficial dorsal vein of the penis. After draining blood from the superficial veins of the penis, it empties into the great saphenous vein.
- Intermediate Venous system – This system is combined with the deep dorsal and circumflex veins of the penis. In addition, this system traverses beneath Buck’s fascia. This intermediate venous system drains blood from the glans, distal two-thirds of the penis, and corpus spongiosum. Moreover, it empties into the prostatic venous plexus.
- Deep venous system – This system includes the cavernous and crural veins. These veins originate between the corpora cavernosa and the crura of the penis. They drain blood from the proximal one-third of the penis and empty into the internal pudendal vein.
Innervation of the penis
The penis is innervated by the S2-S4 spinal cord section and spinal ganglia. In addition, the skin and glans of the penis receive its sensory and sympathetic nerve supply through the dorsal nerve of the penis. The glans of the penis can be seen in the penis image. It is one of the branches of the pudendal nerve. Moreover, parasympathetic nerve supply is provided through the cavernous nerves originating from the peristaltic nerve plexus. This nerve is responsible for the vascular changes that stimulate erection.
Medical conditions associated with the penis image:
The penis is one of the important structures for the maintenance of sexual activity. Any structural or functional problem may lead to serious problems. Here is a list of medical conditions associated with the penis. These problems may require serious medical intervention to deal with the root cause. To understand the medical conditions related to penis, we must know it’s anatomy using the penis image. Let us have a look at these clinical problems related to the penis.
- Infections of the penis – the penis is an external organ and is more prone to infections. These penis infections can cause serious symptoms like pain, redness, itching, or swelling. The common infections of the penis include balanitis, posthitis, and phthiriasis.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) – These are the diseases that are transferred through sexual or physical contact with the diseased person. The STDs include syphilis, gonorrhea, and genital warts.
- Erectile dysfunction – This problem arises when the penis fails to achieve proper hardness for the erection of the penis. This clinical condition usually affects the sexual life of a person. An erect penis can be differentiated in a penis image.
- Priapism – This medical condition relates to the abnormal erection of the penis even after the stimulation period is over. It is usually due to the entrapment of blood in the penis. This painful condition may lead to some serious and permanent tissue damage. There are several problems that can arise from this painful condition.
- Chordee – it is a medical condition related to the abnormal curvature at the end of the penis. This condition is most commonly due to the pull of tissue bands over the penis. It is present after birth.
- Urethritis – is a painful condition of the urethra due to inflammation and swelling. This condition may cause severe pain during urination.
- Peyronie’s disease – This medical condition is also related to the abnormal curvature of the penis. It usually arises due to the scar formation under the skin of the penis.
- Penis warts – This disease is related to the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus can induce the formation of warts around the genitals. Moreover, it is a highly contagious virus with transmission through sexual contact.
- Buried penis – is also one of the medical conditions that require attention. This condition arises due to the abnormal excess fat and skin surrounding the penis as in the penis image. This condition makes the penis less visible making it buried under the layers of skin.
- Penile malignancies – These neoplasms or malignancies are extremely rare. Circumcision lowers the chances of penile cancers.
It is very important to take care of the health of the penis. If not properly washed, it may cause several problems. Let us have a look at the health tips to prevent any infection of the penis.
- Wash your penis regularly with some mild alkaline soaps.
- Prevent the use of abrasive products. These abrasive products can irritate the penis.
- Daily check out your penis for any unusual appearance of lumps on the skin of the penis.
- Must go for barrier methods like condoms to prevent any infection.
- Improve your overall health with strong immunity status.
Conclusion
Summarizing the details of the penis image, this organ ensures the complete reproductive cycle and activity in higher vertebrates. According to the anatomical details, the penis image consists of three main parts that are the root, body, and glans. Besides the reproductive organ, the penis also performs the main function during micturition. The external urethral orifice serves as a common opening for both the semen and urine.
This important reproductive structure is also linked with several medical conditions. These conditions may range from simple infections to severe pain conditions. It is necessary to treat these medical conditions as soon as possible. Consult your doctor if you find any problem mentioned above.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is penile pain a serious problem?
Some minor penis problems can also cause penile pain. So, there is no worry about mild pain. But, If you feel persistent pain lasting for hours with other medical conditions, you must consult your doctor immediately.
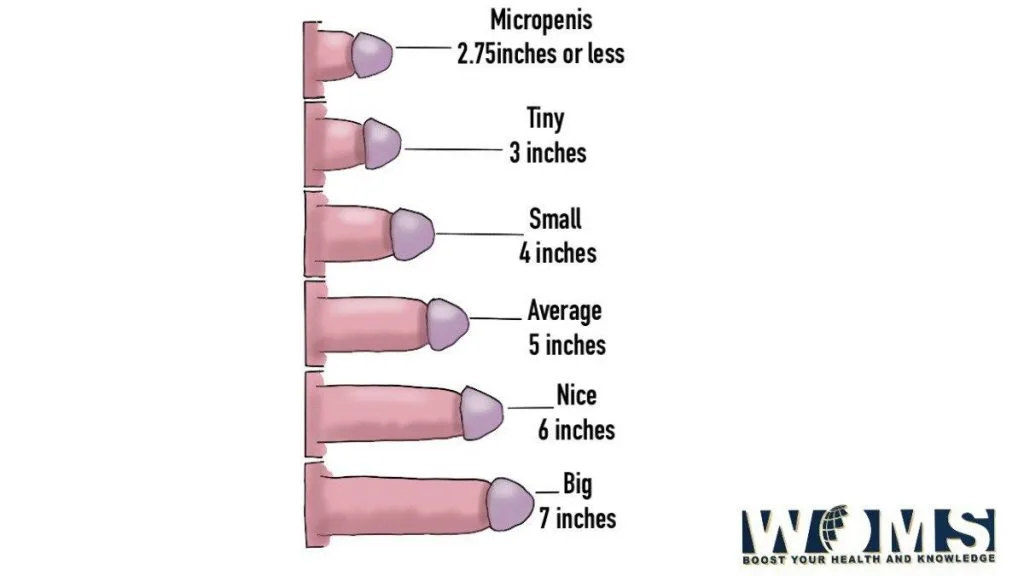
At which age, the penis grows to its maximum size?
During the pubertal phase, the penis, testicle, and scrotum continue to mature. A large-scale study suggests that the growth of the penis is completed up to 17 years.