A Quick Guide to Laboratory Vacuum Pumps
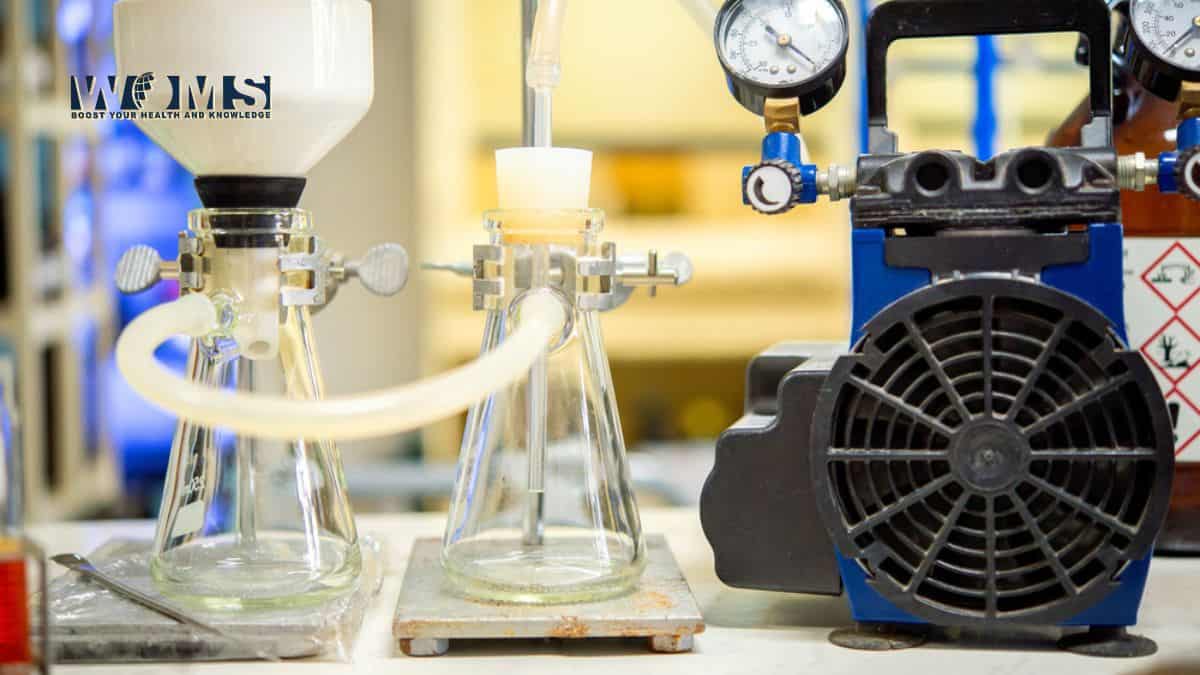

When it comes to research, having all the necessary tools and equipment will ensure accurate results. Some of the equipment you might have ranged from small items such as flasks to more complex systems such as laboratory vacuum pumps, incubators, and more.
This article discusses one piece of equipment: the laboratory vacuum pump. You’ll learn about the definition, types, and functions of laboratory vacuum pumps. Keep reading.
What Is A Laboratory Vacuum Pump?
A lab vacuum pump is a device that’s used to create a vacuum. It does this by sucking in air and gas from an enclosed area, thereby reducing the pressure and allowing for the flow of substances in and out of the enclosed space.
Vacuum pumps are used widely in many industries, such as automotive and medical technology, to assist in the transfer and evacuation of gases, liquids, and particles through vacuum pressure control. Consequently, it’s an essential tool in many applications because of its ability to create a vacuum in an otherwise enclosed area.
Types Of Laboratory Vacuum Pumps
There are several types of laboratory vacuum pumps you can choose from. Some of the major ones include:
Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps
A rotary vane pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses a set of rotating vanes to move fluid from the inlet to the outlet. The vanes are mounted on a rotor that’s driven by an external source, such as an electric motor.
As the rotor turns, the vanes slide in and out of the slots in the pump housing, creating pockets of fluid that are drawn in from the inlet and pushed out through the outlet. The size of the pockets and the speed of the rotor determine the flow rate of the pump. The vanes also help reduce the pressure drop across the pump, making it more efficient.
A rotary vane pump is commonly used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications, such as oil and gas production, chemical processing, food and beverage production, and automotive manufacturing. It’s also used in many other applications, including water and wastewater treatment, vacuum systems, and air conditioning systems.
Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps
This is another type of vacuum pump you can consider choosing. A diaphragm vacuum pump works by using a diaphragm to create a vacuum. The diaphragm is connected to a motor, which causes it to move back and forth.
As the diaphragm moves, it creates a vacuum in the chamber, which draws in air from the outside. This air is then expelled from the chamber, creating a vacuum. This vacuum can be used to move air, liquids, and gases, depending on the application.
A diaphragm vacuum pump has a wide range of applications, thus potentially boosting your return on investment. However, it’s important to understand that this vacuum pump may not be able to support all applications. For this reason, please review your needs first and identify the ideal vacuum pump for your specific application.
Hybrid Vacuum Pumps
These are pumps that have both rotary vane and diaphragm vacuum pump mechanisms. Hence, they still contain oil to lubricate moving parts and ensure a tight seal, as adopted from rotary vane pumps. However, the oil is maintained in a way that eliminates the amount of vapor going through the pump and condensing within the oil. As a result, the oil stays cleaner for longer, and the need for oil changes is reduced.
Although purchasing this type of vacuum pump may be more costly, it can have lower operation and maintenance costs. It can also have higher chemical and corrosion resistance, making it ideal when dealing with a wide range of compounds.
Applications Of A Laboratory Vacuum Pump
There are several applications of vacuum pumps in a laboratory, including the following:
- Aspiration – This is the process of using suction to remove debris, gases, or fluids. For instance, you can use this method to remove spilled laboratory liquid from a bench, ensuring you have a clean and safe place to work on.
- Solvent Degassing – This is a process used to remove dissolved gases from a liquid. It’s often used in the production of pharmaceuticals, food and beverage products, and other products that require a high degree of purity.
The process works by passing the liquid through a vacuum chamber, which reduces the pressure and causes the dissolved gases to come out of the solution. The gases are then removed from the liquid by a variety of methods, such as filtration, adsorption, or distillation.
- Freeze Drying – This process works by removing moisture from a material by freezing it. Once the material is frozen, a vacuum pump is used to remove the moisture from it. The pump creates a vacuum inside the chamber, which causes the moisture to evaporate. The moisture is then collected in a condenser, where it’s also stored for later use.
How To Choose The Right Vacuum Pump
With several types of vacuum pumps to choose from, it can take time to get the ideal one for your needs and expectations. When choosing a vacuum pump, do the following:
Determine Your Budget
Each type of vacuum pump has a different price tag. For this reason, it’s important to ensure you determine your budget for the purchase. Some factors that affect the overall cost of vacuum pumps include the technologies used, complexity, efficiency, and more.
Ensure you research extensively to understand your area’s average price for vacuum pumps. This way, you know what to look for and how to secure the best deal for your situation.
Understand Your Needs
Your unique needs will influence the type of pump you’ll choose. For this reason, ensure you develop a deeper insight into them. Purchasing the wrong vacuum pump will not only affect your research processes, but you may also not be able to even use it. Thus, you may end up losing your money.
Conclusion
Overall, laboratory vacuum pumps are an essential piece of equipment in many scientific and industrial laboratories. They’re used to create a vacuum, which is important for a variety of applications, including distillation, filtration, degassing, and freeze-drying. They’re also used in industrial applications, such as vacuum packaging, vacuum forming, and vacuum impregnation. If you plan to get your own vacuum pump, it’s advisable to research extensively so that you can choose wisely.