Tonsil Cancer: causes, symptoms, prognosis, & treatment
There are more than 200 types of cancers around the world. Tonsil cancer is one of them. We may have not known about tonsil cancer as well as we know about the other ones. To prevent such deadly cancer, we just need to know the causes, symptoms, prognosis, and treatments of it.
We are going to explore the following topics about Tonsil Cancer in the article below:
What is Tonsil Cancer?
Tonsil cancer (carcinoma) is a type of cancer that begins in a person’s tonsil cells. It’s a type of oropharyngeal cancer. It is also classified as throat cancer and also head and neck cancer. This cancer can happen if anyone has had his/her tonsils removed and a small piece of tonsil tissue may be left behind.
Tonsil Cancer causes:
In the past, the known risk factors for this type of cancer were being older and using tobacco or alcohol. People who smoke and drink heavily have a higher chance to contract this cancer in their throat.
These are still risk factors, but nowadays young people who don’t smoke or drink are also developing tonsil cancer. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus associated with sexual contact. Which can be a cause of throat and mouth cancer. HPV-positive people can be affected by the infection who are younger and even if they do not smoke.
Like many other cancers, tonsil cancer causes contribute to a combination of factors, such as one’s genetics, behavior, and environment.
Tonsil Cancer Symptoms and Risk Factors:
Most people do not notice any symptoms until cancer has started to spread. Even many of them may not notice any symptoms even after they’re diagnosed. When symptoms occur, they can match other illnesses, such as swollen throat, mouth pain, and so on.
Here are some basic symptoms that may happen in tonsil cancer:
- A sore throat- lasts for a long time
- Having difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Sudden weight loss
- White or red spots on the throat
- Constant ear pain
- Difficulty swallowing citric foods and drinks
- A mass in the neck or throat
- Blood in the saliva
- Fatigue
Visit a doctor if any of these symptoms last for more than 2 weeks.
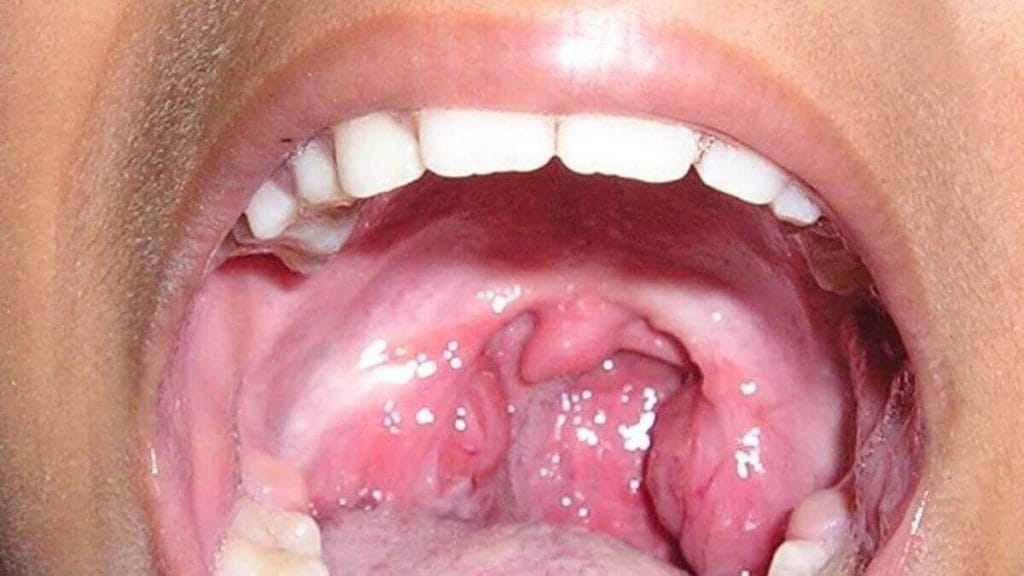
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis begins after the medical history and physical examination results have been inspected, and additional diagnostic and imaging tests may be ordered to confirm or exclude a specific diagnosis. At first, doctors look at the mouth and throat and search for lumps or anything abnormal. Then they suggest some other tests to confirm Tonsil cancer.
These tests may include:
- Lab Test: Blood and urine tests that have changed may point toward cancer.
- Laryngoscopy: The doctor uses a passing thin tube containing a light and a camera down the throat to look for anything abnormal.
- Biopsy: The doctor takes a small amount of tissue to test under a microscope. This is the only way to confirm the cancerous cells’ existence.
- Imaging tests: These may include a
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance images (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- X-ray
If doctors find out the patient has tonsil cancer, they will need to evaluate:
- The cancer stage or how much of the body has been affected
- Its type and grade, which indicates how fast it may grow
This information help doctors determine the best treatment.
Type, Grade, and Stages:
After diagnosing a patient, a doctor will determine some important issues like the type of cancer, how much has it spread, the stage of cancer, and the grade of the tumor with the help of a biopsy report.
Type: There are two types of tonsil cancer:
- Squamous cell carcinoma and
- Lymphoma.
Grade: The grade of cancer is identified by the look of the cells under the microscope and how healthy or unhealthy they are.
Stage: There are 4 stages of tonsil cancer.
- The tumor is less than 2 cm, which is confined to one specific area and has not spread around lymph nodes.
- The tumor is normally 2 to 4 cm but has not spread.
- The tumor is bigger than 4 cm and spread to one lymph node.
- This is the most advanced stage. On stage 4, cancer cells have spread around nearby tissues or other parts of the body except for the throat.
Tonsil Cancer Treatment:
Tonsil cancer treatment depends on the stage and extension of the tumor.
- Surgery: A surgeon removes the precancerous cells or tumors. They also need to remove the tonsils if haven’t had removed them before and additional tissues around the tumor to reduce the risk of leaving cancerous tissue behind.
- Radiation therapy: A doctor will recommend radiotherapy to cut down a tumor before surgery or to kill any remaining cancerous cells after the operation. The therapy stops the growth of a tumor or destroys cancerous cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy kills cancerous cells, but it also damages healthy cells. It is a powerful medication that kills cancerous cells, slows their spread, or shrinks the size of a tumor to make it easier to remove. The doctor may suggest chemotherapy along with radiation therapy without extensive surgery.
- Targeted therapy: Outgoing drugs can target cancerous cells in a correct and selective way. That’s why targeted therapy has fewer side effects than chemotherapy.
- Complications: Complication causes depend on the extent of the procedure, surgery in the mouth, and throat.
After treatment a person may need:
- A feeding tube to supply nutrition
- A tracheotomy, is a hole in front of the throat that helps the patient to breathe
- Dental take-up
- Jaw reconstruction
- Dietary and other monitoring
Prognosis:
There are a few things that have an influence on your tonsil cancer prognosis such as age, health, the stage of cancer, and whether one has HPV. However, smokers appear to have a worse prognosis than nonsmokers, excluding their HPV status. Doctors use statistics to calculate the average chance that a person will survive for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
- 71% of people with HPV do have tonsil cancer.
- 36% of people with HPV do not have tonsil cancer.
The Outlook of Tonsil Cancer:
It is a rare type of cancer. Perception of what is happening and what to expect from treatment can make the process easier.
Factors that impact the outlook include:
- the type of tumor
- the person’s age
- other health conditions
Anyone who notices continuous swelling or other changes in or around their tonsils, must visit a doctor. If anyone finds out that cancer in its early stages often means that it is easier to treat. This improves the chances of recovery.
Tonsil Cancer Survival Rate:
Oropharynx or tonsil carcinoma had a relative 5 years survival rate was 70% but one can not survive periodically.
5-year relative;
- Distant survival rate: 28%
- Regional survival rate: 60% and
- All SEER stages combined survival rate: 90%
Prevention:
People can decrease the chances of having tonsil cancer by;
- quitting or avoiding smoking and tobacco use
- limiting their alcohol intake
- having a vaccination to protect them from HPV
FAQ
Is tonsil cancer deadly?
If caught at an early stage, tonsil cancer is curable. But it is more deadly than any other mouth or throat cancer. Though many people with good immunity power can survive tonsil cancer.
What does tonsil cancer look like?
Tonsil cancer may be identified by symptoms like sore throat, difficulty chewing and swallowing, red or white spots on the throat, etc.
What is the first sign of tonsil cancer?
The first sign is mainly throat aching for a long time and also one tonsil can look bigger than the other one.
Can you survive Stage 4 tonsil cancer?
Stage 4 of the tonsil cancer means cancer has spread to nearby tissues. According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), the relative survival rate of 5-year for stage 4 of tonsil cancer is 39.1%.
Can anyone get rid of Tonsil cancer/ Tonsil carcinoma?
It is a type of oropharyngeal cancer which starts in the cell of one’s tonsil. If the affected tissues can be removed by surgery at early stage, there is a huge chance to get rid of the tonsil cancer.
Read also: Blood cancer