The Splenius Capitis
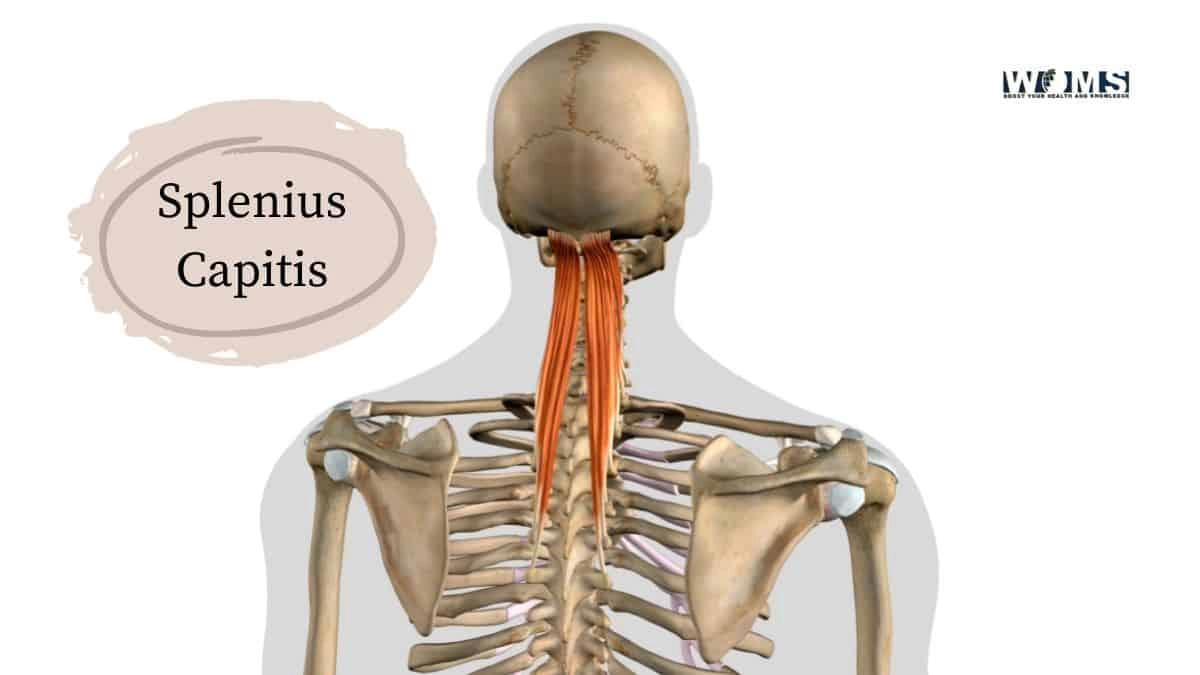
The Splenius capitis is a large muscle in the back of your neck. It attaches to the base of your skull and extends over your shoulder blades, attaching to the spine in a zigzag pattern. The function of this muscle is threefold: it provides stability for the head and neck, assists in reaching forward with one arm while stabilizing from behind, and helps rotate the head when looking up or down.
In this write up we will describe where it originates from, how many different parts there are that can be injured (tendinous insertion), what happens when it gets injured (reduced range of motion), as well as some exercises you can do to help rehabilitate yourself if you have been experiencing pain in this area.
Origin and Insertion:
The upper fibers of the Splenius capitis arise from a narrow tendinous strip called the nuchal ligament, which is located at about mid-height in a deep muscular groove on the posterior surface of the superior articular process and medial to its lateral border.
The muscle passes posteroinferiorly across the side of the neck behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle and then splits into two parts: the ipsilateral superficial part that inserts onto spinous processes of CII through CVI vertebrate ae; the bilateral deep part that attaches to transverse process via longissimus cervicis tendon.
Some muscles involved with motion are meant to move joints or bones around by contracting (shortening) their fibers. Other muscles, like the Splenius capitis, are meant to keep bones and joints in a certain position by contracting (stiffening) their fibers. These are what we call postural muscles.
Injure or Fatigue
When these muscles become injured or fatigued they can no longer do their job properly, which can lead to pain and discomfort. Conditions that may be associated with an injury to the Splenius capitis muscle include neck pain, headache, and restricted range of motion.
If you have been experiencing any of these symptoms it is best to consult with a medical professional who can help assess the root cause of your problem and provide you with a treatment plan tailored specifically for you. However, there are some exercises you can do at home to strengthen muscle fibers. Other muscles, like the Splenius capitis, are meant to stabilize a joint or bone and keep it from moving. This is why when the muscle gets injured, you might experience a reduced range of motion in your neck.
If you have been experiencing pain in this area, please consult with a physical therapist or doctor before starting any exercises on your own.
However, here are five exercises that can help rehabilitate the Splenius capitis:
-Neck retraction exercise: Sit up tall with a neutral spine and gently retract (pull back) your head towards your chest until you feel a stretch in the back of your neck. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat three times.
-Seated chin tuck exercise: Sit up tall with a neutral spine and gently tuck your chin towards the back of your neck. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat three times.
-Seated side bend stretch: Sit up tall with a neutral spine, and bring one elbow across to the opposite shoulder (using both arms if needed) until you feel tension on that side of your body. Keep breathing as you hold this position for 15-30 seconds before repeating then another ride. Do no more than once per day on each side of the body!
-Supine shoulder blade squeeze: Lie on your back with both knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place your hands on top of your thighs with palms down. Squeeze your shoulder blades together as hard as you can for five seconds then relax. Repeat eight times.
-Prayer stretch: Start in a kneeling position with your hands clasped together in front of you as if you were praying. Gently lean forward until you feel a stretch in the chest and hold for 30 seconds before repeating it three times.
Where is Splenius Capitis Muscle Located?
Splenius capitis is a superficial muscle located in the back of the neck and upper part of the thoracic spine.
It starts at vertebrae T-11 and L-12, where it merges with its partner to form the thick posterior arch of the innermost fibers (atlas) before descending as one unit down through two regions: first as deep as levator scapulae muscle then as superior fibers merging again just below the origin of the trapezius muscle.
Splenius capitis inserts into the mastoid process or spinous processes for lower cervical and upper thoracic vertebrae muscles. The muscle is innervated by the posterior rami of spinal nerves C-III, C-IV, and C-V.
What are the functions of the splenius capitis muscle?
The primary function of this muscle is to extend the head and neck. It also assists in lateral flexion (bending to one side) and rotation of the head. Finally, it helps stabilize the cervical spine.
What are some common injuries or issues that can occur with this muscle?
One potential injury is a strain or spasm in the muscle due to overuse or sudden stretching. This can cause pain and stiffness in the neck region. Another issue that can occur is called “crick in the neck” or stiffness in this area that can cause pain when tilting your head to one side.
What are some stretching exercises for this muscle? no sharp pains while exercising?
Have you ever heard about splenius capitis pain before? As always, before engaging in any new exercise routine consult with a medical professional first! A simple stretch recommended by experts is placing both hands behind the back and clasping them together so you have something stable to lean against as shown here: Another option, if you’re feeling adventurous, is yoga poses such as extended child pose (shown below):. In gentle cases of injury though it’s best not to overdo it at first – just go easy on yourself and start slow. As you progress feel free to challenge yourself more regularly but remember to not push your limits too hard!
What are some strengthening exercises for this muscle?
Let us now talk about splenius capitis pain exercises. Strengthening the muscles in your back is a great way to support proper form and posture while lifting weights or engaging in athletic activities. There are exercises that help in relieving splenius capitis pain after sleeping. A simple option that you can do at home with just a few household items includes squeezing a tennis ball between both hands as shown here: This will help target those muscles when they’re called upon during various motions so remember to squeeze before, during, and after any activity.
Splenius Capitis Origin and Insertion
The origin of splenius capitis is located in between the spinous process and ligament nuchae. The insertion sites these muscles the is at mastoid part of the occipital bone these before the superior nuchal line. Splenius capitis can be found by palpating the posterior cervical region with fingers extended along the spine downwards from the midline to the rds. scapula.
It connects itself around the upper thoracic vertebrae by inserting into spines just below level T12-L14. This muscle acts as a rotator or extensor for the head while also playing an important role during forwarding flexion movement against resistance applied on its dorsal aspect over the r shoulder girdle where it gets attached anteriorly through the static base the of skull
How do you treat splenius capitis?
The treatment of splenius capitis is based on the activity causing the pain. Splintinaan was a with a cervical collar, heat and anti-inflammatory medication may help to depend on the severity of the injury. Nonoperative management often relieves symptoms in most cases but it can take up to 16 weeks for full recovery following an acute sprain or strain (pain lasting less than three months).
If your condition fails to respond after conservative care has been tried, then surgical decompression with muscle transfer procedures are options for patients with long-standing unresolved neck pain that is not relieved by physical therapy alone.
Surgery is also an option for patients with severe muscle weakness.
Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve neck range of motion, strength, and endurance. A physical therapist will also teach you how to stretch and strengthen the muscles around your spine. Exercises that can help relieve tension in the muscles of your neck and upper back include:
- gentle stretching exercises for the neck and shoulders (neck rolls, shoulder shrugs)
- Hamstring stretches
- calf raises
- pelvic tilts
- side-lying leg lifts
- low back stretches (cat/cow pose, child’s pose)
If you are experiencing pain or discomfort associated with splenius capitis, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment options such as splinting and physical therapy, which may provide relief for most patients. If conservative care fails to improve your symptoms, surgery may be necessary.
Physical therapy can help you regain strength and range of motion in the neck and upper back muscles. Exercises that relieve tension in these muscles can also be beneficial. Consult a doctor before starting any exercise program.
Splenius Capitis and cervicis
Splenius capitis and cervicis are two of the many muscles in the human body. They are responsible for rotating and extending the head, and also help to extend the neck. Both muscles originate in the spinous processes of cervical vertebrae C-three through C-six and insert into the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The splenius capitis has a tendinous origin, while the splenius cervicis has a fleshy origin.
The primary difference between these two muscles is that the splenius capitis crosses over both sides of the head, while the splenius cervicis only crosses over one side. This means that when either muscle contracts, it will rotate or extend only that side of the head to which it attaches.
The splenius capitis is a powerful muscle and is responsible for a large percentage of the total extension torque produced by the cervical spine. It can be easily injured, however, due to its location and function. Tenderness or pain in the neck region is common symptoms of an injury to this muscle.
Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and compression followed by rehabilitation exercises. With proper treatment and care, most people make a full recovery from an injury to the splenius capitis muscle.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the anatomy and function of the splenius capitis muscles, let’s take a look at some of the potential injuries that can occur. The most common injury to these muscles is small focal, degenerative changes in the insertion fibers occurrence
Symptoms Splenius Capitis Pain
Splenius Capitis Muscle Syndrome typically mimics the respective pain reference patterns of temporal tendinitis and migraine headache. The painful headache starts at the lateral margin of the superior nuchal line and medial to the mastoid process.
The reference areas of pain are described as follows;
- The rear of headaches and hurt.
- Lateral temple headache.
- Retro-orbital headache and pressure.
- Aching pain above the eye.
- Aching pain in the cheekbone under the eye.
- Eye hurts and is sensitive to bright light.
- Pain radiates to the neck, shoulder, and arm at times.
- Nausea and vomiting when pain is intense.
Do read: The Smallest Bone In Human Body
Medical Advice On Splenius Capitis
The Splenius capitis muscle is a small, thin muscle located in the back of the neck. It has two tendinous origins and is inserted into the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae. The muscle fibers run vertically and cross over two joints: the atlanto-occipitaltal joint and the atlantoaxial joint.
The Splenius capitis muscle helps to extend and laterally flex the head and neck. It also assists the n rotation of the head to the opposite side. The main function of this muscle is to maintain posture by stabilizing the head and spine.
The Splenius capitis can be easily damaged due to its location and function. Symptoms of a strained or torn Splenius capitis muscle include pain in the neck and upper back, headache, and difficulty turning the head.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. The Splenius capitis can be treated with rest, ice, and compression therapy. Physical therapy may also be recommended to help strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve the range of motion. Surgery is rarely necessary for a strained or torn Splenius capitis muscle.
The main function of the Splenius Capitis muscle is to maintain posture by stabilizing the head and spine which can easily be damaged due to its location and function. Symptoms of a strained or torn Splenius Capitis muscle include pain in the neck
FAQ
What is splenius capitis?
Splenius capitis is a back muscle. This long, thin band of skeletal muscle runs up and down the neck under the trapezius muscles to move your head from side to side or nod “yes” and rotate it forward and backward (flexion). The muscle is named after its broad, flat tendon of insertion (the part that attaches to the vertebrae), which resembles a diaphragm.
What are the Origins and Insertions of splenius capitis?
The origins of “attachment sites” for this muscle include all parts between Cervical Vertebrae seven through twelve, typically including Atlas (C0) | Axis (C-A= two bones in your neck)| Transverse Processes| Inferior Nuchal Line| Spines of Thoracic Vertebra T11 & T12 | Lateral third of Iliac Crest| External Occipital Protuberance.
The insertions or attachment site of the splenius capitis is located at two areas of the skull. The more superior site is called origin, and it’s found at the spinous process of CIII vertebrae (also known as the Vertebral Spine). This attachment point will form a majority part of this muscle body. The second insertion or attachment site can be found on the mastoid process just behind the ear lobe are