Medical Waste Managing: A Comprehensive Guide from Creation to Safe Disposal

Medical waste is an inevitable byproduct of healthcare activities, ranging from routine patient care to advanced medical research. However, improper management of this waste can pose significant risks to public health and the environment. From contaminated supplies to hazardous materials like pharmaceutical waste and sharp objects, handling medical waste effectively is crucial to minimize contamination and ensure healthcare compliance solutions that maintain strict environmental and safety regulations.
Understanding the Creation and Segregation of Medical Waste
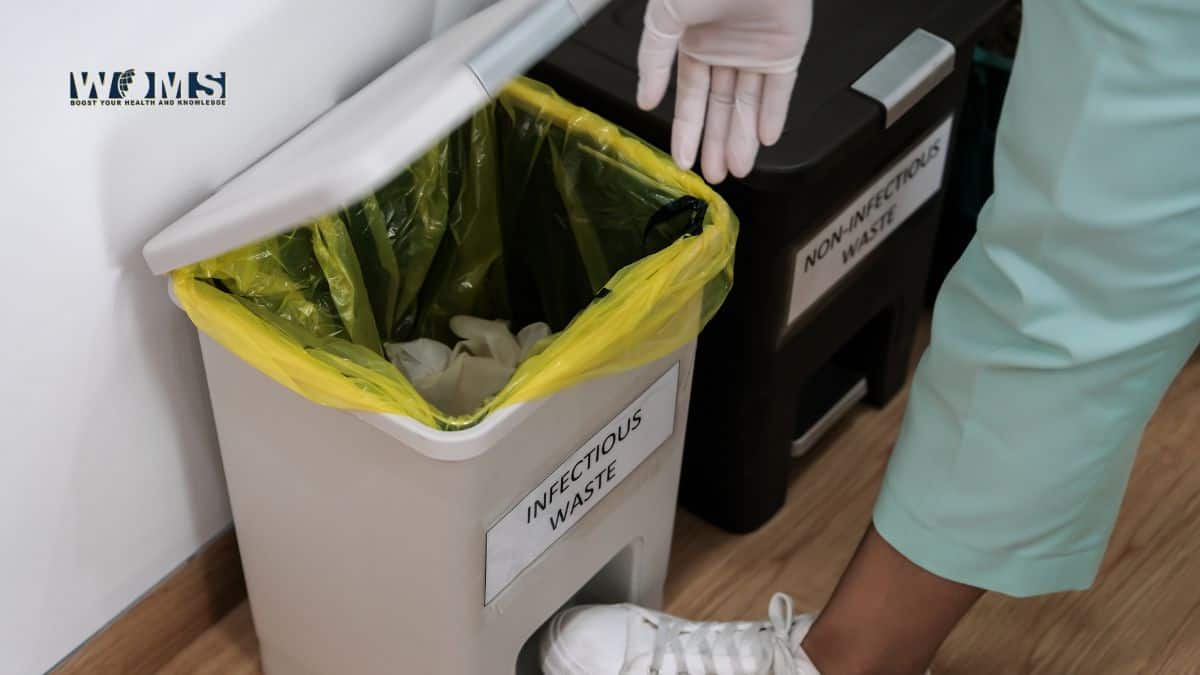
Medical waste is generated across a wide array of healthcare settings, including hospitals, dental offices, research laboratories, pharmacies, and even veterinary clinics. The first and most critical step in managing this waste is segregation—separating different types of medical waste based on their composition and the associated risks they pose. This process involves sorting materials into categories that dictate their treatment, disposal, and handling methods.
For instance, sharps such as needles and scalpels must be placed in puncture-proof containers designed to prevent accidental injury or contamination. Biological waste, including tissues or bodily fluids, requires sealed, labeled bags that prevent leakage and cross-contamination. By adhering to proper waste segregation protocols, healthcare facilities can ensure that each type of waste receives the appropriate treatment while minimizing the risk of contamination and reducing the costs associated with improper disposal.
If waste is not properly segregated, the consequences can be severe. Mixed waste can lead to cross-contamination, which may complicate the treatment process, compromise public health, and increase the costs of disposal. Therefore, establishing a clear, systematic segregation plan is paramount in any healthcare environment.
Safe Storage and Handling Within Healthcare Facilities
After waste has been segregated, it must be safely stored within the healthcare facility. Medical waste must be kept in designated areas that are secure and well-ventilated to prevent exposure to harmful substances. These storage areas should be isolated from areas where patients, healthcare workers, or visitors frequent to ensure safety at all times.
Proper ventilation in these storage areas is crucial to prevent the buildup of dangerous fumes, particularly when dealing with pharmaceutical waste or chemicals. Moreover, these storage zones should be equipped with security measures such as locked doors to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the risk of accidents. It’s also essential that all personnel handling medical waste are trained in safety protocols to avoid exposure to hazardous materials.
Transportation of Medical Waste: Meeting Stringent Standards
Once medical waste is properly sorted and securely stored, it must be transported to a designated treatment or disposal site. This process requires licensed waste management companies that specialize in handling hazardous materials. These companies employ specialized vehicles designed for safe transport and are responsible for ensuring that medical waste reaches its destination without posing a risk to public health or the environment.
The transportation of medical waste is subject to stringent regulations to ensure the safety of workers, the public, and the environment. This includes using vehicles that are equipped with proper containment measures to prevent leakage or spillage during transport. Additionally, the entire transportation process is monitored and regulated to ensure compliance with national and international safety standards.
Treatment Methods for Neutralizing Hazardous Medical Waste
Once medical waste reaches a treatment facility, various methods are employed to neutralize or destroy harmful components. Different types of medical waste require different treatment processes. For example, infectious waste, which may contain dangerous pathogens, is often treated through autoclaving. In this process, high-pressure steam sterilizes the materials, rendering them safe for disposal.
Pharmaceutical waste, which can be toxic or environmentally damaging, is typically incinerated. Incineration involves burning the waste at high temperatures, turning it into ash that can be safely disposed of in landfills. Chemical waste, which may consist of hazardous solvents or reagents, may undergo chemical disinfection or microwave treatment, depending on the nature of the materials.
Each treatment method is selected based on the waste’s composition and the safest, most efficient way to neutralize its risks. This careful, step-by-step process helps mitigate the harmful effects of medical waste on the environment and public health.
Final Disposal: Ensuring Safe Disposal Practices
After treatment, medical waste is ready for final disposal. If the waste has been rendered non-hazardous, it can be safely deposited in landfills or other approved disposal sites. In the case of incinerated waste, the resulting ash is typically placed in secure landfills designed to contain potentially harmful substances. It is critical that disposal methods comply with environmental regulations to avoid any further risk to the environment, particularly when dealing with toxic or persistent materials.
The final disposal phase also includes adhering to all relevant legal requirements, ensuring that any waste that cannot be safely treated or neutralized is handled according to strict guidelines. This ensures that no medical waste ends up in places where it could cause long-term environmental damage or pose a public health risk.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach to Medical Waste Management
Effectively managing medical waste is an intricate and multi-step process that requires careful attention at every stage, from its creation to its final disposal. Segregation, safe storage, transportation, treatment, and disposal are all interconnected, and any lapses in one stage can have a cascading effect on the safety and compliance of the entire system. By adhering to best practices and regulatory standards, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce the risks associated with medical waste while ensuring that they remain compliant with local, national, and international regulations.
Proper medical waste management not only helps protect public health but also plays a critical role in safeguarding the environment. As healthcare practices continue to evolve, the management of medical waste will remain a key issue that demands ongoing attention, innovation, and diligence.
For further insights into medical waste management processes and regulatory guidelines, please refer to the accompanying resource.